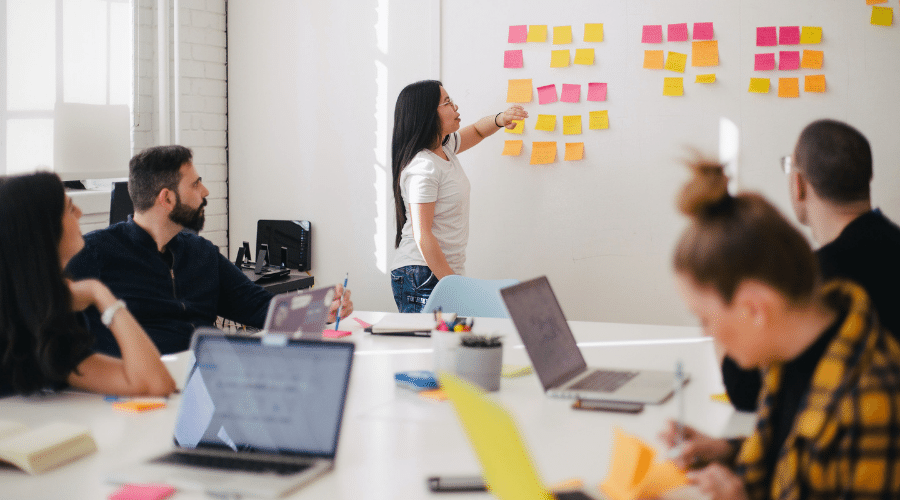
Project management methodologies supported by project management tools define the project’s specific tasks, their distribution among employees, supervision over execution, and control of their interdependencies.
What is a project management methodology?
A project management methodology is a process that a project manager uses to plan, execute, and deliver a project. A project in project management is a set of actions linked by complex relations, having their beginning and end in time and leading to a common goal. Every project has to consist of three elements: budget, action plan (e.g. milestones), and specification. The budget is the resources needed to perform the undertaking, the action plan is a specific roadmap of a project and the specification is a description of the final effect and the method of its accomplishment.
Framework in project management
The project management methodology provides a clear framework for managing a project. This includes defining the roles and responsibilities of each project team member, setting deadlines, and establishing clear milestones. Second, a project management methodology helps to ensure that all stakeholders are kept informed of the project’s progress. This allows for early detection of any potential problems and allows for timely intervention if necessary. Finally, a project management methodology helps to ensure that the project is completed on time and within budget. By using a well-defined methodology, a project manager can increase the chances of success for their project.
The main types of project management methodologies
Agile in project management means iterating and incremental work organization. Production of the ordered object is carried out in an agile and interactive manner, involving frequent interaction with the client and reacting to its suggestions. Agile focuses on the client’s satisfaction to a much greater extent than the original project assumptions. Therefore, it is a perfect tool whenever the client is unsure at the beginning about the desired effect or wants to have an option to order and accept changes. Agile works well if the revision of assumptions based on later difficulties is necessary.
Agile project management is a flexible approach that emphasizes continuous iteration and collaboration between team members. While it is often used in software development, it can also be adapted to other types of projects. If you are looking for a project management methodology that can be customized to fit your needs, it may be a good idea to implement agile project management. You may be surprised at how well it works for you.
Agile is divided into several types, and the actual selection of the most appropriate model depends on the size of the enterprise, level of project complexity, and many other factors. What makes project management using Agile different is that it is simple and flexible, while concurrently observing the principles of other methodologies, e.g., Lean. It is said to be one of the most popular management methods that work well for a fixed budget and deadline.
Lean production is intended to optimize production, minimizing the need for buffers and accumulation of resources. It helps reduce the costs of business and the negative environmental impact of the enterprise, as well as helps increase productivity and improve product quality. Lean is sensitive to standstills, unpredicted supply difficulties, and imperfections in project assumptions.
Waterfall (also referred to as cascade) management model consists of the break-down of tasks into the following linearly consecutive phases. Their specifications depend on the results achieved in the previous test. Its consecutive phases are concept, initiation, analysis, design, construction, testing, implementation, and maintenance.
The waterfall methodology is a project management approach that is widely used in many industries. The approach is based on the principle of moving from one stage of the project to the next in a linear fashion, with each stage being completed before moving on to the next. This approach can be very successful if a project manager carefully plans each stage and make sure that all stakeholders are aware of their roles and responsibilities.
The waterfall is a completely different approach than Agile—it is a cascade model which, thanks to its repeatability, provides great, and sometimes full, foreseeability of what will happen in the course of the project. This allows for the creation of an exact plan, a delivery schedule, and, thus, the determination of a specific completion date. This also gives us information about the exact project cost. This project management methodology proves itself in the management of high-risk activities, where analysis and tests are always in demand. This happens, for instance, in the banking, insurance, and health care sectors.
Kanban (meaning “signboard” or “billboard” in Japanese) is a methodology of work organization in the project used for the first time in Japanese factories by Toyota to reduce the need for storage of subassemblies and to optimize repeatable production cycles. Currently, it is also used for flexible project management. Specific tasks are organized in the form of “post-it notes” in three groups: “to do”, “in progress” and “completed”. Each of them has been assigned performance requirements and deadlines, making identification and elimination of problematic areas easy.
MoScoW is also the methodology of management, based on activity prioritization. The main goal is to reach an agreement as regards the meaning of the particular project elements. MSCW comes from the first letters of words: must, should, could, won’t. When running a project, we choose the elements that are most important to us and those that have to be performed. This way, the team is focused only on the most important aspect of the project. This strategy works great for IT projects.
Scrum is one of the main agile methodologies. It is distinguished by its division into sprints—maximum one-month project development iterations after which the next operating version of the project is delivered. Changes made in each sprint should bring noticeable changes for the users and, thus, planning of work to be performed in it by priorities is very important.
Scrum is a project management methodology that emphasizes teamwork, collaboration, and flexibility. A scrum team is typically small and consists of cross-functional members who have the skills and knowledge necessary to complete the project. The scrum framework is designed to be adaptive and allow teams to change course as necessary to achieve the best possible outcomes. One of the key benefits of scrum is that it allows teams to move forward quickly and make progress even when facing challenging tasks. In addition, scrum promotes transparency and open communication, which helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goal. If you are looking for a project management methodology that will give your team the freedom to be creative and adaptable, scrum may be the right choice for you.
Scrumban is a Scrum and Kanban hybrid. The specific tasks are organized into sprints in which a standard or modified board is used, dividing them into categories. Scrumban also allows for long-term (bucket size) planning. It is based on the system of three “buckets” through which the specific work elements must go before they sprint to the board. Usually, an annual division is applied (e.g., new market penetration, deployment of another product). When the company decides to launch the plan, it goes to the semi-annual bucket where the requirements and assumptions are determined. After moving to the three-month bucket, it is broken down into transparent unit tasks.
PRINCE 2 (Projects In Controlled Environments) is built on products that are standardized and repeatable. It allows employees to improve their competencies within the enterprise and develop a common approach, terminology, and documentation for similar orders.
PMBOK (Project Management Body of Knowledge) assumes that each project has its lifetime-a series of stages between initiation and closure. In the current version, we distinguish 49 types of processes divided into five interacting groups: initiation, planning, implementation, monitoring, and control, as well as completion processes. Furthermore, the processes are assigned to ten knowledge areas, such as time, quality, cost, or HR management. Despite high formalization, PMBOK allows for certain flexibility in project work organization.
Six Sigma approach was applied for the first time in the 80s at Motorola. The main goal of the method is to reduce the chance of a defect to 3.4 per million chances, which translates into the distance of six sigma (standard deviations) from the central value of the adopted probability distribution.
5-day sprint method is a very popular project management methodology. It is used by many top companies and organizations. 5-day sprint method helps you complete an entire project in 5 days. It is a very effective way to manage a project. You can use it for any type of project – both small projects or large projects. In this methodology, five days is all that is required to begin with a project idea, work through its project tasks, and reach the testing phase.
Critical chain project management (CCPM) is a project management methodology that focuses on reducing project duration by identifying and addressing project risks. critical chain project management is based on the theory of constraints, which states that any system is limited by its weakest link. In the context of project management, this means that the project schedule is only as good as its longest task. To reduce project duration, critical chain project management seeks to address the risks associated with these longest tasks. This is done by identifying the critical path – the sequence of tasks that determines the minimum project duration – and then adding buffers to protect against risks. By mitigating risks, critical chain project management can help shorten project timelines and improve project outcomes.
Kaizen methodology is based on a Japanese concept. It is defined as the continuous enhancement of completed work and personal efficiency. This philosophy promotes the continuous development process that is also identified with improvement. It consists of the engagement of all employees in a constant search for improvement ideas for all areas of the organization. The goal is to eliminate current problems, prevent their recurrence in the future, and create innovative solutions. This applies to all people in the organization—both the members of the management and the employees. The concept assumes that continuous development regards every sphere of life-not only professional, but also private and social.
In the management aspect, Kaizen has two main functions: standard maintenance and improvement. Maintenance refers to the current technology level, operating standards, and management in such a way that everybody can adhere to the relevant operating procedures. Improvement, on the other hand, refers to activities enhancing the standards.
Kaizen means small, gradual efforts leading to changes. Staff training, efforts, commitment, self-discipline, communication, and teamwork are the foundations of Kaizen. It is a problem-solving methodology. The important thing is that the difficulty has to be both recognized and understood. The proper solution requires the collection and analysis of relevant data. Collecting data regarding the current status helps understand the essence of the problem, decide what to concentrate on, and what to improve first.
Which project management methodology is best?
Which methodology is the best depends on several factors, including the nature of the project, the team involved, and the resources available? For example, waterfall project management is well-suited for projects with well-defined requirements and predictable outcomes. On the other hand, the agile project management methodology is more flexible and can accommodate changes more easily. The key is to select the methodology that best fits the needs of the project. Often, a hybrid approach is the best solution.
Agile project management methodology in 2022
Agile project management methodology is a very popular approach to projects, gaining ground and support in 2022. Agile, Scrum, Kanban – these are all terms always associated with the notion of agility in project management systems.
What is agile project management?
Agile project management is an iterative and incremental approach to managing projects. Projects in agile management are typically characterized by short development cycles, close collaboration between team members, and a focus on delivering value to the customer. The method of agile project management was first developed in the software industry, but it has since been adopted in a variety of other industries.
What is Agile project management methodology?
Agile project management methodology is a process that helps organizations manage projects in a more agile way. The agile approach emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and customer involvement throughout the project lifecycle. In addition, the agile workflow can help to improve communication and collaboration among team members and increase customer satisfaction.
Unlike traditional methods, which are often linear and inflexible, agile processes harness change. As a result, they have become well-suited for today’s fast-paced, ever-changing business environment.
There are a variety of agile project management methodologies that can be used, depending on the specific needs of the project. The most common agile methodology is Scrum, which is based on a team-based approach. In Scrum teams, each team member has a specific role to play and is responsible for completing tasks within a set timeframe. Other popular agile methodologies include Kanban and Lean.
What is the difference between agile and traditional project management methodology?
Agile project management is often compared with traditional project management. The difference is that style of agile management is considered to be less rigid and bureaucratic, more agile and responsive to change, while traditional project management is more focused on planning and control. While there are benefits to both approaches, agile project management is generally considered to be more beneficial for projects that are subject to frequent change or uncertainty.
Agile project management certification
Successful implementation of agile project management methodology requires that all team members are properly trained in the chosen methodology. Agile project management certification is designed for project managers who want to learn how to apply agile project management practices to their work. The certification program covers topics such as Scrum methodology, product backlogs, and sprint planning.
Upon completion of the certification program, project managers will be able to apply agile principles to their work to improve project efficiency and effectiveness. In addition, project managers who are certified in agile project management will be better positioned to lead agile teams and deliver successful projects.
Difference between Waterfall and Agile methodologies
The agile methodology approach to projects emerged as a response to the need for better and more efficient project management. Market changes, changing client needs, and, most importantly, the ever-increasing demand for new software development projects, had a significant impact on agile project management.
The Waterfall model involves full project control — from its beginning, through its intermediate stages, to the delivery of the project to the client. It is a structural approach that requires the right breakdown of the project, determination of resources, a schedule, or potential other additional aspects.
What is Agile project management with Scrum?
Scrum is one of the most popular agile project management methods, and it helps to ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget. The Scrum process is divided into sprints, or iterations, each of which has a specific goal. At the beginning of each sprint, the development team plans which tasks need to be completed. During the sprint, scrum team members work together to complete the tasks and produce a working software product. At the end of the sprint, the product is demoed to the customer, and feedback is collected. This feedback is then used to plan for the next sprint. By following this iterative process, agile teams can deliver valuable software products that meet customer needs.
Agile project management with Scrum is a process that helps organizations manage projects in an agile way. agile project management methods are based on the Agile Manifesto, which advocates for adaptive planning, early and continuous delivery, constant feedback, and close collaboration between stakeholders.
To implement agile project management with Scrum, organizations need to have a clear understanding of the Agile Manifesto and its principles. They also need to have a team of skilled professionals who are familiar with agile methodology and can help guide the organization through the agile process.
How does agile project management work?
Numerous interesting solutions and scientific articles were published from 1994 to 2001. The beginning of this century brought the Manifesto for Agile Software Development. Commonly known as the Agile Manifesto, it is a collection of all the principles and guidelines for agile project management. At present, agile practices are mostly associated with Agile, but we cannot forget about Scrum (often equated with Agile, even though there are several differences) or the popular Kanban. As part of the publication of the Agile Manifesto in 2001, four key assumptions and values were formulated at the outset:
- People and interactions first, processes and tools second.
- Functioning software over comprehensive documentation.
- Cooperation with clients first, official arrangements and negotiations second.
- Ongoing response to changes first, implementation of the assumed plan second.
To put it more traditionally, agile project management methodologies demonstrate a flexible approach to principles, plans, processes, or any other arrangements. It is an agile approach based on making quick and ad hoc decisions. Agile emphasizes communication and soft skills much more. It is the team developing the software that makes decisions, delegates tasks to its members, or determines how to execute them. There are no rules that cannot be touched when changes are needed – everything unfolds during a meeting or conversation. If variables are required, in Agile, they have introduced them right away.
Agile in practice
In practice, Agile assumes that we cannot plan and determine all project-related actions at the start, so it relies on work divided into short cycles. In most cases, cycles in agile projects are called sprints, which last from 1 to 4 weeks. During every sprint, the team prepares a part of the software and, thus, assembles the entire system into one whole. As a result, you can communicate with your client much more efficiently, arrange certain variables on an ongoing basis, and push forward with the project with pretty great force.
Let us remember that in the Agile model, it is the team that is the key aspect of work on the given sprint. It is the team members who distribute tasks among themselves and, importantly, have the proper competencies to work in the given field. Therefore, they are the software and identify strongly with it. It is not only another ordinary task to be done in a project; it is creating the entire step-by-step to then put all those components into one whole. It is conducive to the motivation of employees and their eagerness to work every day as they feel an actual part of the entire project—they have a real impact on what the entire system will look like. The employee’s motivation and values are what make agile project management stand out.
Project management methodologies examples
When developing software in the Waterfall model, the project team focuses on the entire project from the very beginning and, thus, differentiates several basic stages. In most cases, these are:
- System planning: from A to Z, the entire system must be planned at the start
- System analysis – e.g., analysis of requirements and an implementation plan
- System design—elaboration on all individual structures
- Implementation – production, i.e., code creation
- Testing is a testing process regarding every element of the system
- System deployment – supplying the client with the full product
The creation of software is largely reliant on a pre-made framework that has been planned out in advance. If a phase does not produce a good result, the team must go back and improve the earlier components.
It is the team that determines what small steps – the sprints described above for Agile – to take to deliver the whole. Each sprint pertains to different tasks to be done for sustainable software development. A sprint takes a short period – usually a minimum of one week and a maximum of one month. Every sprint has a number assigned (and a name referring to the topic of the work performed). The Agile workflow commonly involves regular and cyclic meetings at which the team discusses the tasks completed during the sprint and specifies what they will work on now, usually during the next sprint. This way, the entire software is created from small blocks, which are then combined into one whole. The team is the key aspect of the entire project in Agile; the team members are the project – they make decisions, determine tasks and complete them.
We have surely repeated a lot of information when describing the waterfall and agile methodologies, but we wanted to show the key differences and, to an extent, compare the two most common approaches to projects – Agile and Waterfall. We are certain that you will no longer have any problems with defining those key project-related differences.
What is the difference between Agile and Scrum?
Scrum and Agile are very similar topics, falling within the agile project management approach. In short, Agile projects are approached iteratively – you complete a part of your project, review it, respond, conclude, and proceed to further tasks. In this case, you introduce variables on an ongoing basis, so there is no key plan here: you just work – as the name suggests – in an agile manner. Agile is an approach to project management, and Scrum is a specific methodology defining principles of operation. The principles that are used in working on Agile projects, to be exact. The Scrum methodology provides us with nomenclature and steps to be taken in specific situations. We use it all in Agile, but it is formulated in the Scrum methodology. It’s simple and similar, yet you have to understand the difference.
Scrum project management methodology
Scrum is a popular project management methodology that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and constant communication. Unlike traditional methods, which often involve lengthy planning periods and rigidly defined roles, scrum relies on small, self-organized scrum teams to get work done. This approach can be especially effective for complex projects that require frequent adjustments. In a scrum environment, team members are constantly in contact with each other, sharing information and making sure everyone is on the same page. This allows for quick course corrections when necessary and prevents problems from getting out of hand. As a result, scrum can help to ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
What is Scrum project management methodology?
Scrum is the most widespread of so-called agile project methodologies based on the Agile Manifesto. According to the rules of the Scrum methodology, product development comes in short, consecutive stages called “Sprints.” Iterative process control over the project allows for efficient and innovative creation of the product and its maximum match to the client’s expectations.
The first mentions of the Scrum methodology appeared as early as 1986. Its main assumptions were presented by Hirotaka Takeuchi and Ikujiro Nonaka in the article “The New Product Development Game,” published by Harward Business Review. In the ’90s, Scrum has developed thanks to people like Ken Schwaber and Jeff Sutherland, who is 1995, during the conference in Austin, Texas, jointly presented a work dedicated to the methodology. Six years later, the same people presented the most known to-date manifesto connected with the IT work methodology – The Agile Manifesto.
Scrum framework
The scrum framework is based on three key principles: transparency, inspection, and adaptation. These principles help to ensure that scrum teams can quickly identify and correct errors, resulting in higher-quality software. In addition, scrum teams are typically small and highly effective, with each member playing an important role in the scrum team’s success.
The scrum team is composed of a scrum master, product owner, and development team. The scrum master is responsible for facilitating the scrum process and ensuring that the scrum team adheres to the scrum principles. The product owner is responsible for defining the product backlog and prioritizing items in the backlog. The development team is responsible for delivering the product increment. Scrum is an iterative and incremental process that helps teams deliver value quickly and efficiently.
Sprints, or work in processes
According to the Scrum methodology, called frameworks by its creators, the project scrum teams work in Sprint processes, which usually take from 1 to 4 weeks. Sprints are iterations consisting of repeating respective elements cyclically and fixedly during the entire process of the project. The effect of each process should be the delivery of a subsequent version of the product with implemented changes that are visible to the user.
Sprints stages
Each sprint begins with Sprint Planning, during which prioritized tasks are sent for each process. An inherent element of sprints is so-called daily scrums, i.e., everyday scrum team meetings during which the work progress is checked and decisions on further actions are made. The next stage is Sprint Review, i.e., checking the increment of the product and feedback. The sprint ends with a retrospective, i.e., a summary which aims to help in improving the subsequent iterations.
Roles in Scrum Project Management
Individual characters play a key role in the Scrum methodology. These are Product Owner – a person representing the client, responsible for making decisions linked to product development and project duration, The Scrum Master creates the right environment for work and the scrum team, motivating employees in daily, short meetings.
Scrum teams
Scrum teams are cross-functional teams of experts responsible for developing software through the scrum process. Scrum is an iterative and incremental approach to software development that emphasizes collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. The scrum team is typically composed of a scrum master, product owner, and development team. The scrum master is responsible for facilitating the scrum process and ensuring that the team adheres to scrum values and principles. The product owner is responsible for defining the features of the product and prioritizing the backlog. The development team is responsible for implementing the features and delivering working software at the end of each sprint. Scrum teams typically hold stand-up meetings every day to discuss progress and impediments. They also hold sprint planning, sprint review, and sprint retrospective meetings at the beginning, end, and middle of each sprint. To be effective, scrum teams need to have good communication, collaboration, and problem-solving skills.
Advantages of the Scrum methodology
Implementing the agile methodology may provide a plethora of benefits that would otherwise be unavailable.
the project with traditional methods. Above all, Scrum allows you to:
- changes regularly in the project during its performance—both in existing and future functionalities.
- fully monitor the product’s development – each Sprint concludes with the release of a new version of the product for the client to test and make changes for implementation in the next Sprint.
- perform the project in the fastest and most efficient way thanks to corrections made regularly and, hence, better adjust the product to the client’s expectations.
- change the scope of the project and even close it at any time—for example, in the situation of a reduced budget,
- minimize the expenses connected to formalities—there is no need to create comprehensive project documentation.
- increase the team’s morale—thanks to self-organization, the project participants have more room for experiments, and their relations are based on colleagueship, which translates to better efficiency.
Scrum and project budget
The Scrum method is related to the possibility of introducing changes and adding new functionalities. This, in turn, may lead to unexpectedly exceeding the budget. In effect, the end-product, though comprehensive, may also not meet the initially assumed tasks.
Scrum principles
Scrum project management is a type of Agile methodology that is popular in the software development industry. The key principles of Scrum are transparency, inspection, and adaptation. These principles are achieved through a set of roles, events, and artifacts. One of the most important aspects of Scrum is an investment in training. This investment ensures that scrum team members have the knowledge and skills necessary to be successful. While Scrum can be challenging to implement, the investment in training is essential for its success. With the right training, Scrum can help your team to be more agile and adaptable, leading to more successful projects.
When is it worth working with Scrum?
When it comes to project management, Scrum is best suited to projects that are complex and subject to change. That’s because scrum is built around the idea of constant adaptability and evolution. With scrum, everything is focused on the product being developed, and the scrum team works in short “sprints” to make incremental improvements.
This approach can be very helpful in situations where the requirements are constantly changing or where there’s a lot of uncertainty about what needs to be done. Because scrum is so flexible, it’s easy to make changes as new information arises, which can help keep the project on track. If you’re working on a complex project that is likely to change over time, scrum project management may be worth considering.
5 days sprint – project management method
Project management time in 5 days, that is one hundred and twenty hours-this is the time you need to complete virtually any project and, in more detail, turn the idea into an operating, often sales-generating, prototype. Three specialists working for the largest corporations in the world have proved the 5 days project management methodology to be efficient. These three men are Jake Knapp, John Zeratsky, and Braden Kowitz.
Sprint aims to find the final solutions as quickly as possible, even if it requires extra work at a later stage. Sprints of this type enable the team to see the ready product and the client’s response to it. It is not necessary to make costly investments, contribute a lot of money, lose tons of time, and only later see that the idea stinks and clients will not accept it.
5-day project management sprint examples
The book written by Knapp shows step-by-step, the consecutive stages of action and includes many examples of successful implementations of the 5 days sprints. According to Knapp, each working day should last from 10:00 to 17:00, including one hour for a lunch break and a short coffee break. A typical project sprint means six hours of active work. “Starting at 10:00, we give each person time to check their e-mails and find out what is going on before the day starts.” To conduct and complete the project in this period, each morning, all team members switch off their phones and cut themselves off from everyday distractions. If it is really necessary to answer the phone, it must be done outside the meeting place. This way, you can introduce a new product to the market, improve the client support quality, and find alternative solutions for the current state of affairs in the company.
Two successful projects in which the 5-day sprint was used are:
- Development of a website and internet shop for a well-known coffee brand, Blue Bottle Coffee. The website is a beta version that was ready in five days, but what matters is the fact that information about coffee, its drinking rituals, etc., was revealed during the sprint.
- Creation of a robot used in the hotel, service, and medical industries. Namely, the Relay robot, manufactured by Savioke. The robot was ready to perform the first tasks three weeks after the sprint.
Implementation of 5-day project management methodology
Each such action consists of five stages, out of which each is assigned to one day:
- Monday: the creation of a project map and goal selection. A map can be, e.g., a website layout and the goal – online sales of coffee;
- Tuesday: development of professional, competitive solutions: it can turn out that the first idea is not the best one, so we can find an alternative solution;
- Wednesday: brainstorming and selection of the option which allows for the optimum achievement of goals set on Monday;
- Thursday: the creation of a realistic prototype-it does not have to be the entire website, complete product, or complete service; it is just about the functionality that is most important to us. In the case of the Relay robot, it was a driving model with a display and an installed camera so that clients’ reactions could be registered;
- Friday: prototype tests among target clients, i.e. nothing else, but reaching out to our target group and showing them its operation. Here, it is important to collect feedback and analyze it. This day is a real “to be or not to be” for a project. It could turn out that our assumptions were wrong and the prototype just did not meet the client’s expectations. What do we gain? We save money and implementation time. The incurred costs entail the work of a maximum of seven people who participate in the sprint plus materials that may be necessary for the creation of the beta version.
How to build a project team?
An optimum team consists of:
- decision maker– CEO, company owner, a person who can take the most important implementation decisions;
- financial expert —someone who can manage how to finance the subsequent stages, where to get money, and so on: can be, e.g., the financial director.
- marketing expert —somebody who can sell the idea further, at the same time giving it personality traits that are consistent with the message and mission of the company;
- customer specialist—someone who is familiar with our clients, knows who the target persons are, and what the target segments are.
- logistics and technology expert—somebody who can easily handle the technical issues and will find necessary solutions;
- project specialist is somebody who creates or creates other company products and who understands the philosophy and method of their creation.
Software for Project Management
The deployment of any project management methodology in businesses is easier when dedicated software is used. The project management software allows the creation of plans and task groups for employees. During project performance, the software provides the status of the project and the costs sustained. This considerably simplifies the supervision over the performance of individual tasks both for the management staff and for the client and shortens the communication path in matters concerning the given project.
A perfect example of such software is the IC Project. This is a cloud-based tool that serves to manage separate tasks and the whole business comprehensively. It allows dividing projects into tasks and task groups and managing them using the Kanban method. Thanks to it, you can create a task, assign employees to it, and set deadlines or guidelines easily. Moreover, IC Project features a built-in calendar, instant messenger, and file manager, which makes it easier to gather appendices in the dedicated folders. Its additional advantages are an invoicing module and the possibility of co-creating a project with the given client and functions that allow for the monitoring of deadlines, employee absences, supervision of task performance, and the provision of communication channels.
Kanban boards tool for agile project management methodology
Kanban is also strongly associated with the agile approach to project management. Kanban is a task-based work tool enabling agile task-based work in a project. It is used when creating new sprints, distributing tasks, and controlling performance on an ongoing basis. Kanban boards allow to write out and delegate tasks quickly with a notification system. It lets you monitor deadlines better as the application will remind you of them and help you stick to them using different deadline views. Kanban tools feature options to set priorities, divide tasks into single actions to do, and provide communication within the given task or the entire sprint. Kanban will support the visualization of processes and current work as well as store the entire project history in the agile project management methodologies.
Application of project management methodologies tools
Project management methodologies tools are mostly used in such enterprises as:
- marketing agencies,
- software houses,
- enterprises providing various services,
- consulting enterprises,
- design enterprises,
- human resources.
Project management methodologies glossary
Project
A project is a unique undertaking leading to the creation of a unique product. Therefore, it differs from repeatability-oriented production and services. Depending on the adopted methodology, it can be broken down into smaller one-off or cyclic tasks.
SMART features
SMART features are the acronym Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. That’s what a well-formulated project objective should be characterized with.
Kickoff meeting
The participants of the kickoff meeting (starting meeting inaugurating the project) are the team members and the client. Its purpose is to collect key information – targets, assumptions, deadlines, budget, etc. – regarding the order. Its essential elements include discussion and building a positive and encouraging atmosphere.
Roadmap
The roadmap is another term to describe a schedule, plan, or scheme of actions oriented at the accomplishment of the given goal. It is usually employed in strategic planning at the high organizational level and is dedicated to long-term activities.
Feasibility study
The feasibility study is an analysis and assessment of the project’s potential. Its purpose is the objective identification and strengths and weaknesses of assumptions as well as related opportunities or threats. It comprises the determination of resources required to complete the project as well as its chance for success.
Critical path
The critical path is a series of specific activities – a delay in any of them results in an extension of product completion. It is the longest possible series of tasks ordered chronologically where the next one can be started only after the previous one is completed.
Project manager
The project manager is the person responsible for the accomplishment of its goals. The project manager is responsible for planning, coordination of tasks, and project closing and, therefore, he or she has to be active at all stages of work.
Scoping
Scoping is a procedure involving the determination of the scope of the entire project or its part. In certain situations, it may be required by the law, e.g. in the scope of assessment of project environmental impact.
Gantt Chart
Gantt chart is a graph used in management. It is based on project breakdown into tasks and time planning. To improve transparency, the tasks may be marked with different symbols.

Milestone
A milestone is an event in the project schedule that summarises the set of tasks or a phrase (e.g. supplying the beta version to the client). Its occurrence may entail the need or option to decide on the further form of the project.
Spaghetti plot
The spaghetti plot is used in lean methodologies to visualize in-house product paths at the early product or production stage. It facilitates tracing weaknesses generating losses due to wrong allocation and extension of transport or decision paths.
Burn down chart
The burn-down chart is used in Agile methodologies, e.g. Scrum. It is used to visualize work remaining to be done over time, enabling the determination of trends and timeliness control.
Kanban board
The Kanban board may have a physical or digital form. “Post-it notes” are attached to it, symbolizing the specific tasks – each with its performer, assumptions, and deadline assigned. Traditionally, it is divided into three categories: “to do”, “in progress” and “completed”, and changing the status of the given task means moving it.

Poka-yoke
Poka-yoke (in Japanese poka – a mistake, yokeru – proofing) is a mitigation method for the risk of defects and accidents resulting from mistakes. It assumes that mistakes are the fault of processes, not people.
Muda, Mura, Muri
Muda (waste), Mura (unevenness), and Muri (overburden) are three types of losses occurring – and requiring elimination – in Lean methodologies. Their identification and implementation of optimization solutions is a necessary step in enterprise development.
Risk register
The risk register is one of the documents used in the PRINCE 2 method. It contains information on threats, their analysis, countermeasures, and status. It is updated by the manager at almost any project stage and influences the planning of further tasks to be performed by the team.
Parkinson’s law
Parkinson’s law was formulated in 1955. It is the adage that “work expands to fill the time available for its completion”. At first, it was used for public administration, but it also applies to project management. One of its implications is the fact that an employee who is given a specific amount of time to complete a task will complete it as late as possible.
Deadline
The deadline is the final due time for the completion of a task or entire project. The deadline is also the milestone point.
Summary
It is worth remembering that the client is not only our partner, but they also finance our venture. A satisfied client will not only pay the invoice on time but also recommend our work to other people. Every project management methodology benefits from a skillful building of relationships with customers. Effective collaboration on a project leads to increased trust between both parties and allows them to keep the promises made. To implement a project management methodology effective communication is necessary. Project management is a process that helps to ensure that teams can work together effectively to complete a project. By working together, teams can identify potential problems and come up with creative solutions.
Project management methodologies streamline work through the breakdown of big undertakings into smaller units that are easier to control and complete as well as ordering them on the timeline to meet project management expectations. Whether it is agile scrum or another type, the implementation of a project management methodology well suited to the specifics of the enterprise and projects run by it requires cooperation and communication.